Learning from Good Practices of City to City Collaboration: Enhancing Sustainable City Development through the JCM City to City Collaboration
Institute for Global Environmental Strategies (IGES)
Outline
This event sheds light on the JCM City to City Collaboration feasibility studies that have been conducted since 2012. Today, cities and sub-national authorities are acknowledged as important and JCM City to City Collaboration will foster actions and cooperation toward smart, low-carbon and resilient cities. The session shares advantages and lessons learnt by introducing good practice examples from the past JCM City to city collaboration projects. The session invites donor agencies as well as specialists from Asian cities which implement JCM City to City Collaboration as speakers, and the panel will discuss the expectations and the potential of JCM City to City Collaboration.
Program
-
- Welcome Speech
- Professor Hironori Hamanaka, Chair of the Board of Directors, IGES
-
- TAP (Transformative Action Programme) and the future prospect
- Mr. Gino Van Begin, Secretary General, ICLEI International
-
- Y-PORT city city-to-city collaboration - The case from Da Nang
- Ms. Haruka Miki, Policy Researcher, IGES
-
- Asian Development Bank’s support to urban development in Asia
- Mr. Ryuzo Sugimoto, Environmental Specialist, Asian Development Bank (ADB)
-
- Framing presentation about the progress of COP21
- Mr. Kazuhisa Koakutsu
-
- Discussion
-
- [Participants]
- Mr. Gino Van Begin, ICLEI International
Mr. Ryuzo Sugimoto, ADB
Professor Hironori Hamanaka, IGES
Dr. Kentaro Tamura, Senior Policy Researcher, IGES
- [Facilitator]
- Prof. Hironori Hamanaka, IGES
-
- Comments and Q&A
Summary
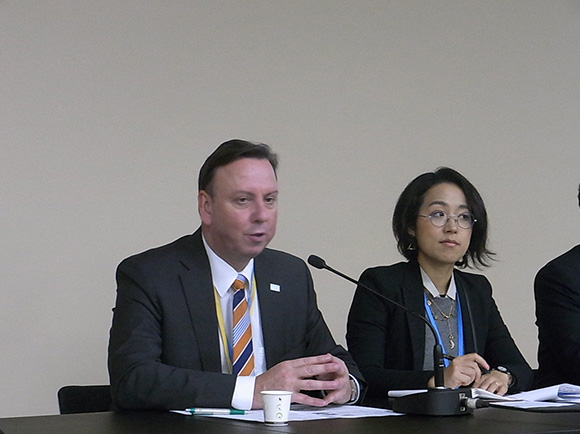
The event was introduced by Hironori Hamanaka, IGES, who explained the increasing importance of the role of the non-state actors such as cities and subnational in climate action. He also mentioned that COP21 UNFCCC Official event on Lima-Paris Action Agenda (LPAA) has introduced city to city collaboration in Asia as an example of good practice.
Gino van Begin, Secretary General, ICLEI, explained ICLEI’s Transformative Action Programme (TAP) which is the show case of local climate action which may be introduced to potential investors.
Haruka Miki-Imoto, IGES, introduced an example of upscaling non-state actors ’action with an example of city to city collaboration between City of Yokohama, Japan and City of Da Nang, Vietnam.
Ryuzo Sugimoto, Asian Development Bank (ADB), presented the menus that ADB finance cities and subnational initiatives. One example was Japan Fund for Joint Crediting Mechanism (JCM).
Kazuhisa Koakutsu, mentioned that foundation of LPAA and Non-State Actors Zone for Climate Action (NAZCA) should be linked with mechanisms under UNFCCC such as Technical Examination Process (TEP), technical mechanism such as CTCN and finance mechanism such as GCF to the actual.
Kentaro Tamura, IGES, suggested the strengthening of TEMs and high level dialogues are essential for promoting NAZCA.
Discussion covered the institutional arrangement to allow the direct access to finance including the usage of Global Environmental Facility (GEF) and the importance of dialogues on different levels of stakeholders in order to promote NAZCA.
Key Messages
The role of Non-State Actors such as cities and sub-national in climate action has been increasing.
Three suggestions to upscale the cities’ and sub-national’s actions.
- Measurement, reporting and verification (MRV): It is essential to make sure that climate action sets sounding Green House Gas (GHG) reduction target and achieve them;
- Financing local action: Mechanism to share risk from projects by cities and subnational as well as long-term commitment from cities and subnational foster investment to local climate action; and
- Linkage between LPAA/NAZCA and UNFCC mechanism: LPAA/NAZCA could be an effective platform to link the cities’ and subnational actions with the existing UNFCCC process and mechanisms such as Technical Examination Process (TEP), Technology Mechanism (Climate Technology Centre Network) and Financial Mechanism (Green Climate Fund.)
Photograph
Reporters
Haruka Miki, Institution for Global Environmental Strategies (IGES)