Exhibition - COP25 JAPAN PAVILION
Deep NINJA
The first practical float measurable in the deeper ocean
than 2000 meters
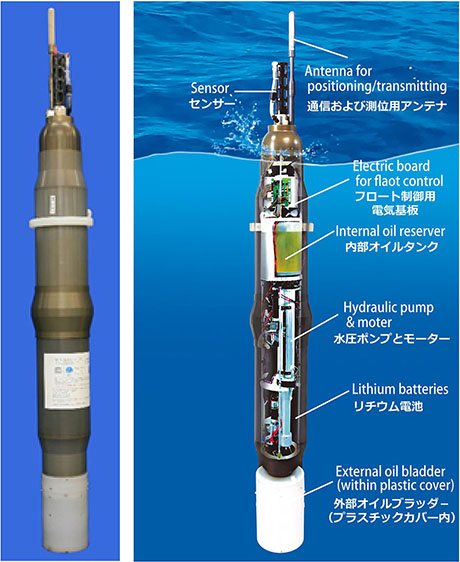

(Left) Deep NINJA and (Right) its inside mechanics.
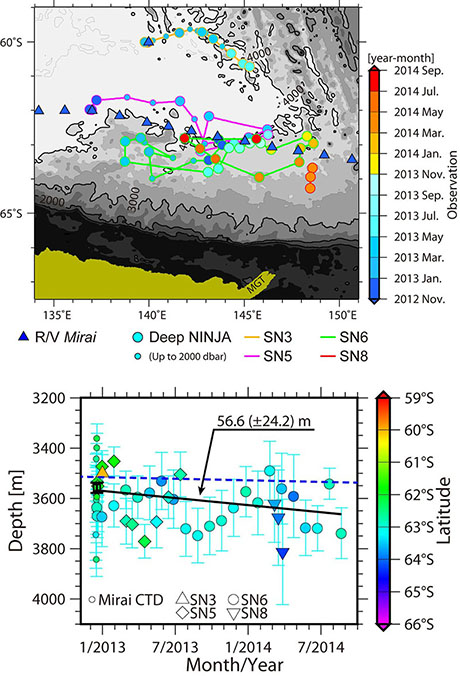
(Upper) Locations of Deep NINJA observations. (Lower) Depth of the upper boundary of Antarctic Bottom Water observed by Deep NINJA floats. The average rate of the change is shown by solid line.
In recent years, the deep ocean has been increasingly recognized as an important component of the global climate system. Hydrographic observations in recent decades clarified deep ocean warming below 2,000m depth, which accounted for about 10-15% of the accumulated heat in the Earth. Such estimations, however, were less reliable than the other climate components; the deep ocean is considered as a major source of uncertainty in the climate system, mainly due to few observations. Now, as several deep floats were introduced, a monitoring array with numerous deep floats, "Deep Argo", is being deployed.
Deep NINJA, which was developed by JAMSTEC with Tsurumi-Seiki Co. Ltd., is the first deep float measurable in the ocean below 2,000m. It can observe up to 4,000m depth, which covers about 90% of the global ocean. Recently, our Deep NINJA fleet observed a rapid decrease of Antarctic Bottom Water in the Antarctic Ocean. Until now, more than 30 units have been deployed in the Pacific, Indian and Southern Oceans to build the global array of Deep Argo.
Exhibit Partner
Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology (JAMSTEC)